
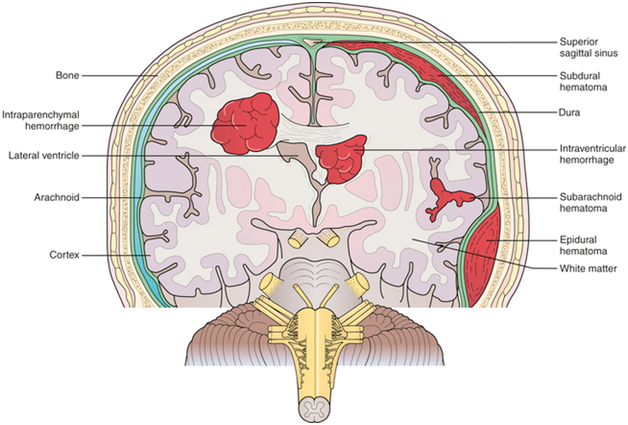
Depending on the cause, some.2. Brainstem hemorrhage is a very serious condition in which bleeding occurs in the stem region of the brain. Another contributing factor for this type of hemorrhage is a congenital, or present at birth, disorder called arteriovenous malformation, in which the blood vessels in the brain stem are abnormal and tangled together in a complex web.Doctors at Southampton’s teaching hospitals have reversed a procedure developed to stem bleeding in the brain to help them save the lives of seriously ill stroke patients.A brain hemorrhage is a type of stroke caused when an artery bursts in the brain, triggering localized bleeding in the surrounding tissue. Check out surgery, symptoms, recovery, treatment, survival rate, causes, and diagnosis.Theyre caused by a weakened vessel that ruptures and bleeds into the surrounding brain.
A blood vessel in your brain has burst, causing bleeding. This fact sheet will help you better understand what is The procedure, known as intra-arterial clot retrieval, restores blood flow without the need for any surgical intervention.Conventionally, stroke patients are treated with blood-thinning drugs through a drip within the first three hours of the onset of their symptoms, but the option is not always successful for those with blockages in large vessels or suitable for those recovering from major surgery, which makes them susceptible to internal bleeding.“Employing a procedure developed to treat ruptured brain aneurysms, we are able to open blocked vessels that cause severe strokes – something much more common than bleeding in the brain,” said Dr John Millar, a consultant neuroradiologist at Southampton General.“Once we locate the blocked vessel, we pass a small metal stent through a micro-catheter, immediately open it and use the same device to remove the clot.”Dr Pam Crawford, a consultant physician and director of stroke at University Hospital Southampton NHS Foundation Trust, added: "With the treatment options for patients who suffer severe stroke limited, being able to remove the clot quickly and effectively is a major advancement and crucial to the chances of survival.”Latest figures show the Trust’s 24/7 stroke service, launched in 2009 to rapidly treat acute or mini-stroke (transient ischaemic attack) through immediate access to a dedicated specialist team, has one of the best survival rates in the country.Every year, each hospital receives a score based on how ill their patients are and how many survive, known as the standardised mortality ratio, with hospitals expected to meet an average of 1.0. The two types of hemorrhagic strokes are intracerebral (within the brain) hemorrhage or subarachnoid hemorrhage.
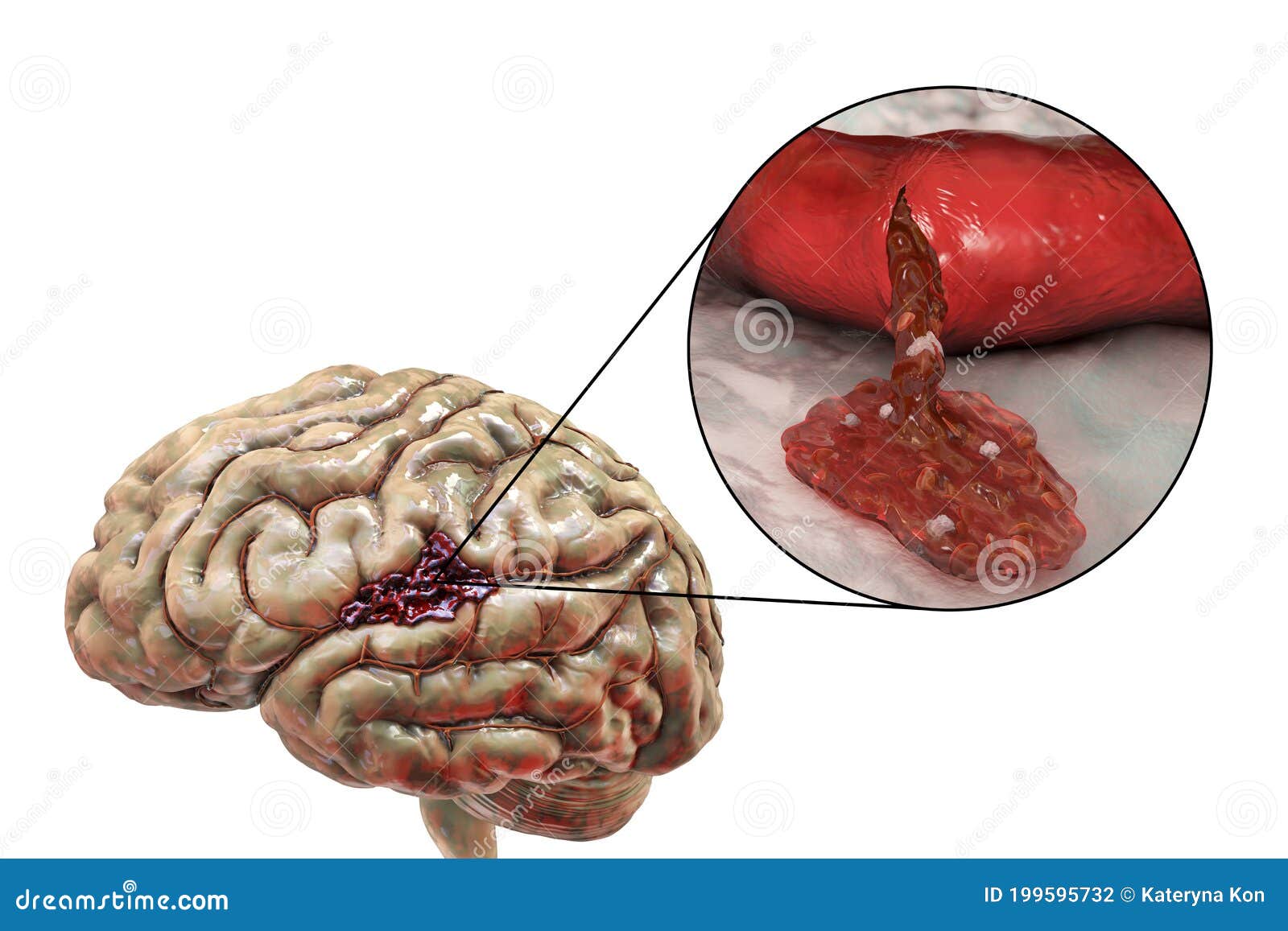
'Worst headache I've ever had'The pain began last December. So when 18-year-old Sulecma started complaining about bad headaches, Mondragon thought the phone was the culprit.Neither would have imagined that the headaches were life-threatening and would require the expertise of UCI Health neurosurgery team to treat their true cause — bleeding in the brain, a rare condition in someone so young. Her daughter, like most teenagers, was often on her phone texting friends and catching up on social media.

But in February, a follow-up angiogram revealed the aneurysm was regrowing. Fifty percent of patients die before reaching the hospital, and those who survive often are permanently disabled,” Lin said.Sulecma was discharged just in time for her family’s Christmas and New Year’s celebrations. Subarachnoid hemorrhages are very dangerous.
“Most parents think the headaches will go away on their own or with ibuprofen, but if your child has a very strong headache, don’t ignore it. Recognizing when a headache needs attentionAlthough brain aneurysms and subarachnoid hemorrhages are extremely rare in people under 40, Lin says it is important to recognize when a headache could be a sign of a more serious condition.“Patients with subarachnoid hemorrhages complain of having the worst headache of their life, thunderclap headache, or headache that is different from any other type of headache or migraine that they’ve ever had,” Lin said. “If you have these types of headaches, you need to go to the ER immediately.”Mondragon advises teenagers and parents to not disregard strong headaches. Sulecma’s latest cerebral angiogram was performed only five months after treatment and showed the aneurysm was more than 90 percent gone. The flow diverter stent also allows for new blood vessel cells to form, sealing off the opening of the aneurysm and healing this diseased part of the artery.Lin is one of the most experienced physicians in the region using flow diversion. This method uses a unique stent that is placed across the opening of the aneurysm to divert the blood away from it.
What happens if a loved one has a stroke on vacation? › What you know know about preventing, treating and spotting stroke › She is looking forward to starting her senior year at Norte Vista High School in Riverside and making plans for college.“I want to become a nurse,” Sulecma said.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
